Introduction:
In the rapidly evolving landscape of communication technology, Short Message Service (SMS) gateways play a crucial role in facilitating seamless and efficient text messaging between various devices and platforms. Whether used for marketing campaigns, transactional alerts, or two-factor authentication, SMS gateways have become an integral part of modern communication infrastructure. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of Sms API, their functions, and their diverse applications in today’s interconnected world.
Understanding SMS Gateways:
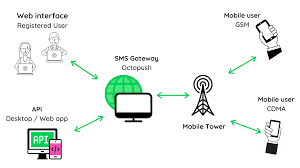
An SMS gateway is a technological interface that allows the transmission of short messages between different telecommunication networks. Acting as a bridge between various messaging applications and mobile carriers, SMS gateways facilitate the delivery of text messages from a web-based platform to mobile devices, and vice versa.
Key Components of an SMS Gateway:
- API (Application Programming Interface): SMS gateways are typically accessed through APIs, enabling developers to integrate messaging functionalities into their applications, websites, or systems. This allows for automated and programmable communication.
- SMPP (Short Message Peer-to-Peer): SMPP is a protocol used for exchanging SMS messages between Short Message Service Centers (SMSCs) and external entities, such as applications or messaging platforms.
- HTTP/HTTPS Protocols: Some SMS gateways support communication through standard web protocols like HTTP or HTTPS, providing a more straightforward integration process for developers.
Functions of SMS Gateways:
- Message Sending and Receiving: The primary function of an SMS gateway is to send and receive text messages. This includes one-way communication, where businesses send messages to their customers, as well as two-way communication for interactive applications like customer support or surveys.
- Number Formatting and Validation: SMS gateways often perform number formatting and validation to ensure that messages are sent to valid and properly formatted mobile numbers. This helps improve the delivery success rate.
- Message Queue Management: To handle large volumes of messages efficiently, SMS gateways often incorporate message queue management systems. This ensures that messages are processed in a timely manner and delivered promptly.
Applications of SMS Gateways:
- Marketing and Promotions: Businesses leverage SMS gateways for marketing campaigns and promotions, sending targeted messages to a specific audience. This direct form of communication has proven to be effective in engaging customers.
- Transactional Alerts: SMS gateways are widely used for sending transactional alerts, such as order confirmations, account notifications, and appointment reminders. This enhances customer experience by providing timely and relevant information.
- Authentication and Security: Two-factor authentication (2FA) and one-time passwords (OTPs) sent via SMS are common security measures. SMS gateways play a crucial role in ensuring the secure delivery of these authentication codes.
- Emergency Notifications: Governments, organizations, and emergency services use SMS gateways to broadcast critical information during emergencies, natural disasters, or other urgent situations.
Conclusion:
In the age of instant communication, SMS gateways serve as the backbone of many essential services and applications. From marketing and customer engagement to security and emergency notifications, the versatility of SMS gateways continues to drive innovation in the way we connect and communicate. As technology advances, we can expect SMS gateways to evolve, providing even more efficient and secure messaging solutions for the digital era.